In 1996, General Motors's EV-1 battery-powered electric car appeared in Saturn showrooms in California and Arizona. Over the next seven years, more than 1,000 models were leased to drivers who wanted to get around without the burden of putting gasoline in their cars. However, GM ultimately decided consumer demand and battery technology wasn't quite up to par, and most of those cars ended up at a crushing facility.
Since the 1990s, the price of fuel has skyrocketed and battery technology has advanced considerably, so GM has decided that it's time to take another crack at the electric car. This time, though, they're doing things a little differently.
Advertisement
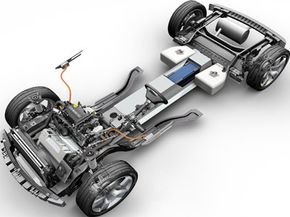
The E-Flex Propulsion System is an all-new platform from GM that's expected to underpin the highly anticipated Chevrolet Volt sedan, due in showrooms by the end of 2010. The system puts what engineers call a revolutionary spin on the electric car -- one that's driven by electric power but can drive for hundreds of miles with the help of an internal combustion engine.
"[E-Flex vehicles require] no support from a gas engine to operate, unlike a hybrid, which cannot operate without the engine," said GM spokesman Dave Darovitz. "Our engine is not directly connected to the wheels and only comes on when the battery is depleted, acting as a stationary, on-board generator to create additional electricity to re-charge the battery and power the car." However, unlike hybrid cars like the Toyota Prius -- which uses a small electric motor for low speed driving and switched to an internal combustion engine for acceleration and faster driving -- GM considers cars built on the E-Flex platform to be electric cars rather than plug-in hybrids.
After a night of recharging (any household power outlet will do), the car's wheels are driven solely by electric power from its battery pack. The gasoline-powered engine is used only to recharge the battery once it runs out of power.
If all goes according to plan at GM, cars powered by E-Flex can run up to 40 miles (64 kilometers) on electric power alone, without using a drop of gasoline. After 40 miles (64 kilometers), the car's initial battery charge is depleted, and the internal combustion engine -- called a range extender -- seamlessly kicks in, operating a generator that charges the battery and keeps the car running on electric power.
In the next section we'll look at the heart of the E-Flex platform -- its battery -- and how much money you'd save with a car that runs on one.
Advertisement