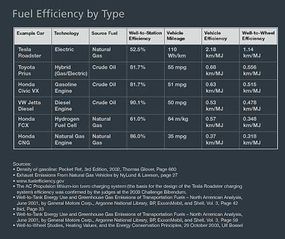
Key Takeaways
- The Tesla Roadster was a revolutionary high-performance electric sports car that offers a quiet but powerful driving experience, utilizing an advanced electric motor and a large battery pack to avoid the use of gasoline entirely.
- Key features included a sophisticated battery system capable of rapid charging and a then-unique regenerative braking system to enhance its efficiency.
- The vehicle emphasized safety with rigorous battery safety tests and integrated fault protections.
When you climb into the seat of a high-performance car that costs six figures, you expect certain things: acceleration that pushes you back into the seat, top-end stereo equipment, road-hugging handling, the throaty roar of a powerful engine and a big budget for the high-octane gas needed to fuel it. Well, the Tesla Roadster has almost all of those aspects covered. It's fast, fancy, handles like a dream and goes like a rocket, but it's virtually silent and it'll never burn a single drop of gasoline. Tesla's first production car is also the world's first high-performance electric car.
Unlike a traditional gasoline-powered car, the Tesla Roadster doesn't contain hundreds of moving parts. It's powered by just four main systems:
Advertisement
- The Energy Storage System (ESS)
- The Power Electronics Module (PEM)
- An electric motor
- A sequential manual transmission

In place of an internal combustion engine, the Tesla Roadster sports a bank of batteries -- the Energy Storage System (ESS). In developing a power source befitting such a high-performance car, Tesla went with technology proven in the laptop computer field -- rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. The Roadster contains 6,831 of them. They weigh about 1,000 pounds in total, and Tesla claims that they provide "four to five times the energy-density stores of other batteries" [ref]. The batteries fit into 11 sectors with 621 batteries each. A separate computer processor controls each sector to make sure all of the charging and discharging is handled smoothly.
The Power Electronics Module (PEM) is a power inverter and charging system that converts DC power to AC power using 72 insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs). This results in a marked increase in power output compared to first-generation electric cars. Under peak acceleration, the batteries can crank out 200 kW of energy -- enough to light 2,000 incandescent light bulbs.
In addition to controlling charge and discharge rates, the Power Electronics Module controls voltage levels, the motor's RPM (revolutions per minute), torque and the regenerative braking system. This braking system captures the kinetic energy usually lost through braking and transfers it back into the ESS. The efficiency and integration of the battery, PEM and motor systems is between 85 and 95 percent, allowing the motor to put out up to 185 kW of power. Aluminum heat dissipation fins and a rear-mounted ventilation port keep the power transistors from overheating.

You can recharge the Roadster in two different ways. An electrician can install a recharging station in your garage. This 220-volt, 70-amp outlet allows for a full recharge in 3.5 hours from a completely dead battery. Tesla likens charging your car to charging your cell phone; you can plug it in at night and have a fully-charged car in the morning. There's also a mobile kit that allows recharging at any electrical outlet, no matter where you are. The length of time it takes to charge using the mobile kit depends on the outlet configuration that you're using (110-volt or 220-volt).
Although auto owners have been driving around for decades with tankfulls of volatile, flammable gasoline in their cars, having 1,000 pounds of batteries behind their head gives some people pause. The recent recalls of lithium-ion batteries used in laptop computers have increased those fears. Tesla has gone to great lengths to ensure the safety of the Roadster's energy system. First, the battery system was extensively "catastrophe tested," which involved heating individual cells until they burst into flames. Each cell is isolated enough from adjacent cells to prevent any damage to them. If one cell overheats, it will not start a chain reaction explosion.
A host of sensors detects acceleration, deceleration, tilt, temperature and smoke. If one senses an abnormal event, like a crash, it immediately shuts down and disconnects the power system. Similar anti-fault protections and sensors are part of the charging system [ref].
Advertisement