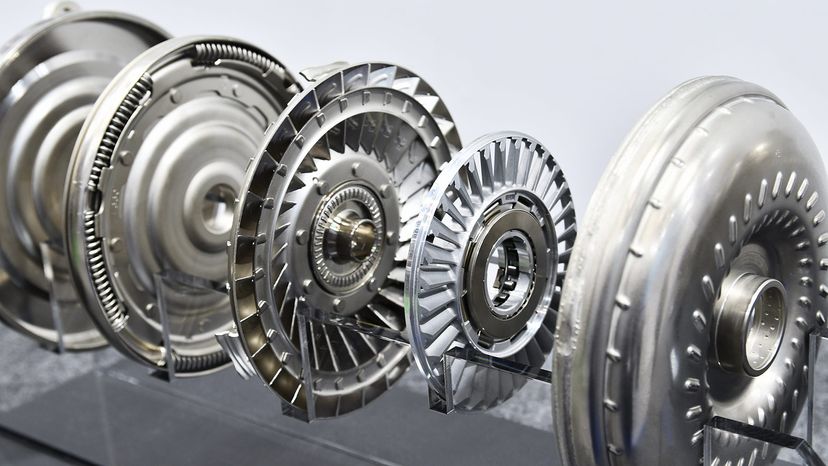
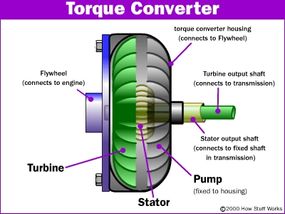
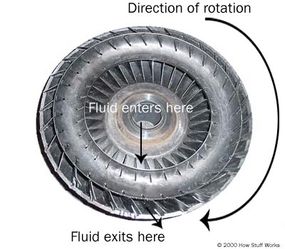
If you're familiar with manual transmissions, you know that an engine is connected to a transmission by way of a clutch. Without this connection, a car would not be able to come to a complete stop without killing the engine. Cars with automatic transmissions have no clutch that disconnects the transmission from the engine. Instead, they use a device called a torque converter. It may not look like much, but there are some very interesting things going on inside.
Turning a car's engine crankshaft produces torque (which is the energy you create by twisting something). Torque is what allows you to accelerate your car. The more torque an engine produces, the faster a car goes. A torque converter allows the engine in a car with an automatic transmission to keep running even as the wheels come to a stop.
Advertisement
In this article, we'll learn why automatic transmission cars need a torque converter, how a torque converter works as well as some of its benefits and shortcomings. The automatic gearboxes we refer to are the traditional type that have been popular in cars since about the 1950s. Newer types of automated transmission, like the semi-manual gearbox and CVT use other methods of power delivery, and don't include torque converters.