Locking and Torsen Differentials
The locking differential is useful for serious off-road vehicles. This type of differential has the same parts as an open differential but adds an electric, pneumatic or hydraulic mechanism to lock the two output pinions together. A permanently locked differential can also be made by using a metal rod to weld both pinions to each other, but this is not advisable for street use.
This mechanism is usually activated manually by a switch and when activated, both wheels will spin at the same speed. Some modern lockers can activate automatically using input from wheelspin-detecting sensors. If one wheel ends up off the ground, the other wheel won't know or care. Both wheels will continue to spin at the same speed as if nothing had changed.
Advertisement
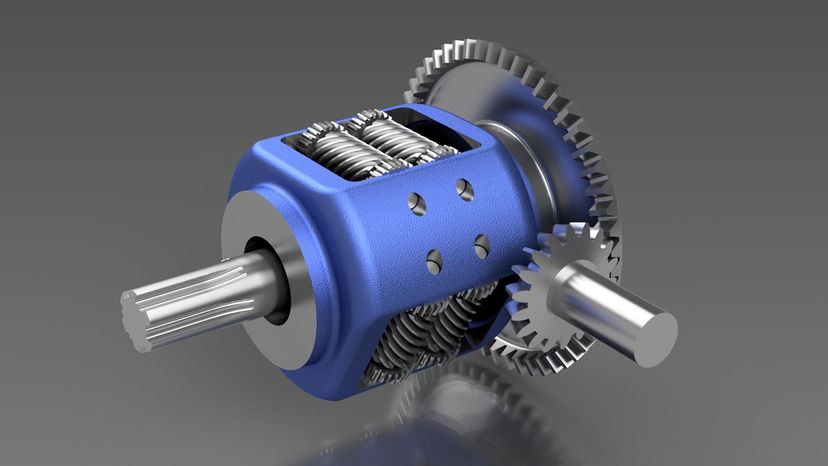
The Torsen differential is a purely mechanical device; it has no electronics, clutches or viscous fluids.
The Torsen (from Torque Sensing) works as an open differential when the amount of torque going to each wheel is equal. As soon as one wheel starts to lose traction, the difference in torque causes the gears in the Torsen differential to bind together.
The design of the gears in the differential determines the torque bias ratio. For instance, if a particular Torsen differential is designed with a 5:1 bias ratio, it can apply up to five times more torque to the wheel that has good traction.
These devices are often used in high-performance and all-wheel-drive vehicles. Like the viscous coupling, they are often used to transfer power between the front and back wheels. In this application, the Torsen is superior to the viscous coupling because it transfers torque to the stable wheels before the actual slipping occurs.
However, if one set of wheels loses traction completely, the Torsen differential will be unable to supply any torque to the other set of wheels. The bias ratio determines how much torque can be transferred, and five times zero is zero.